Products Description
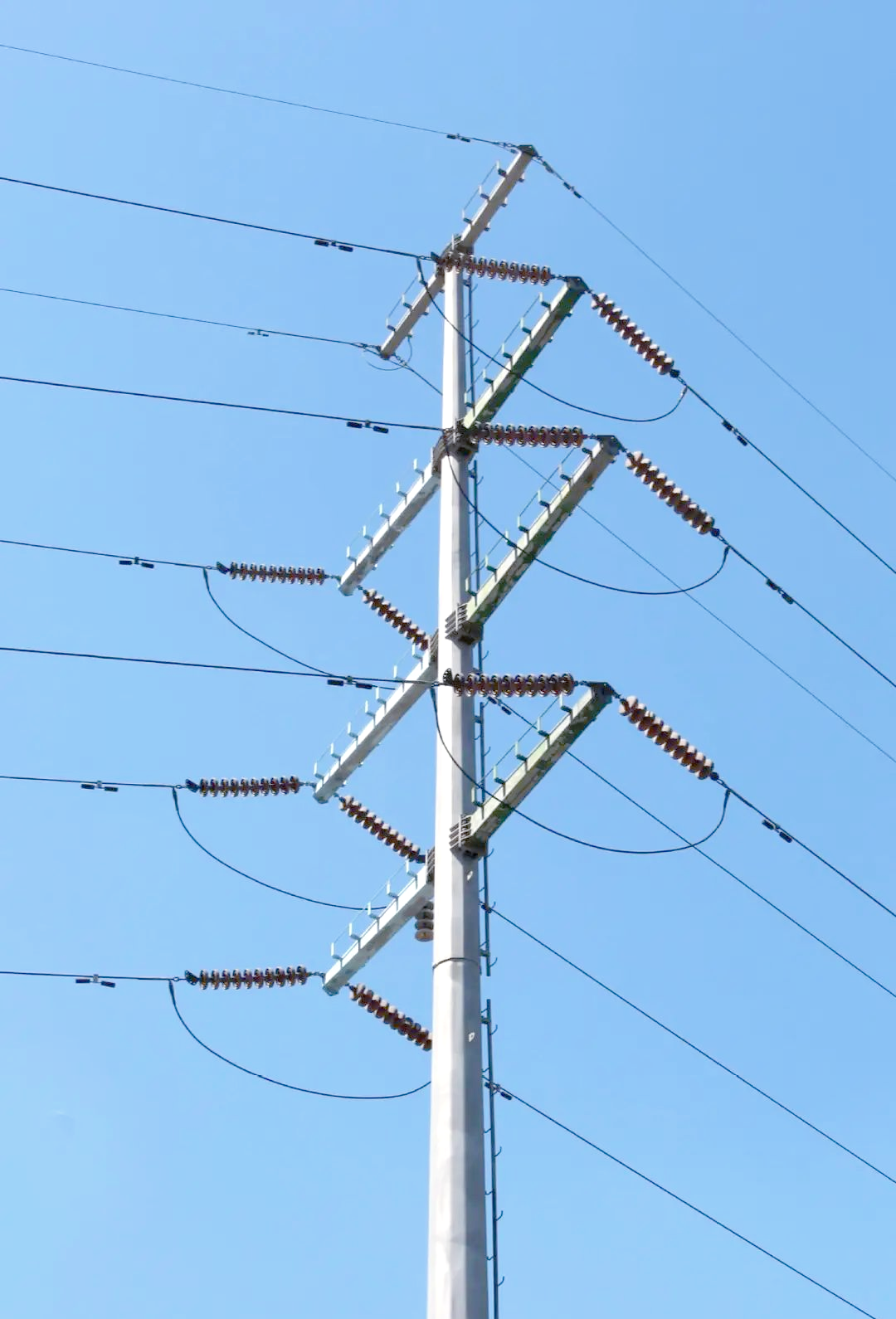
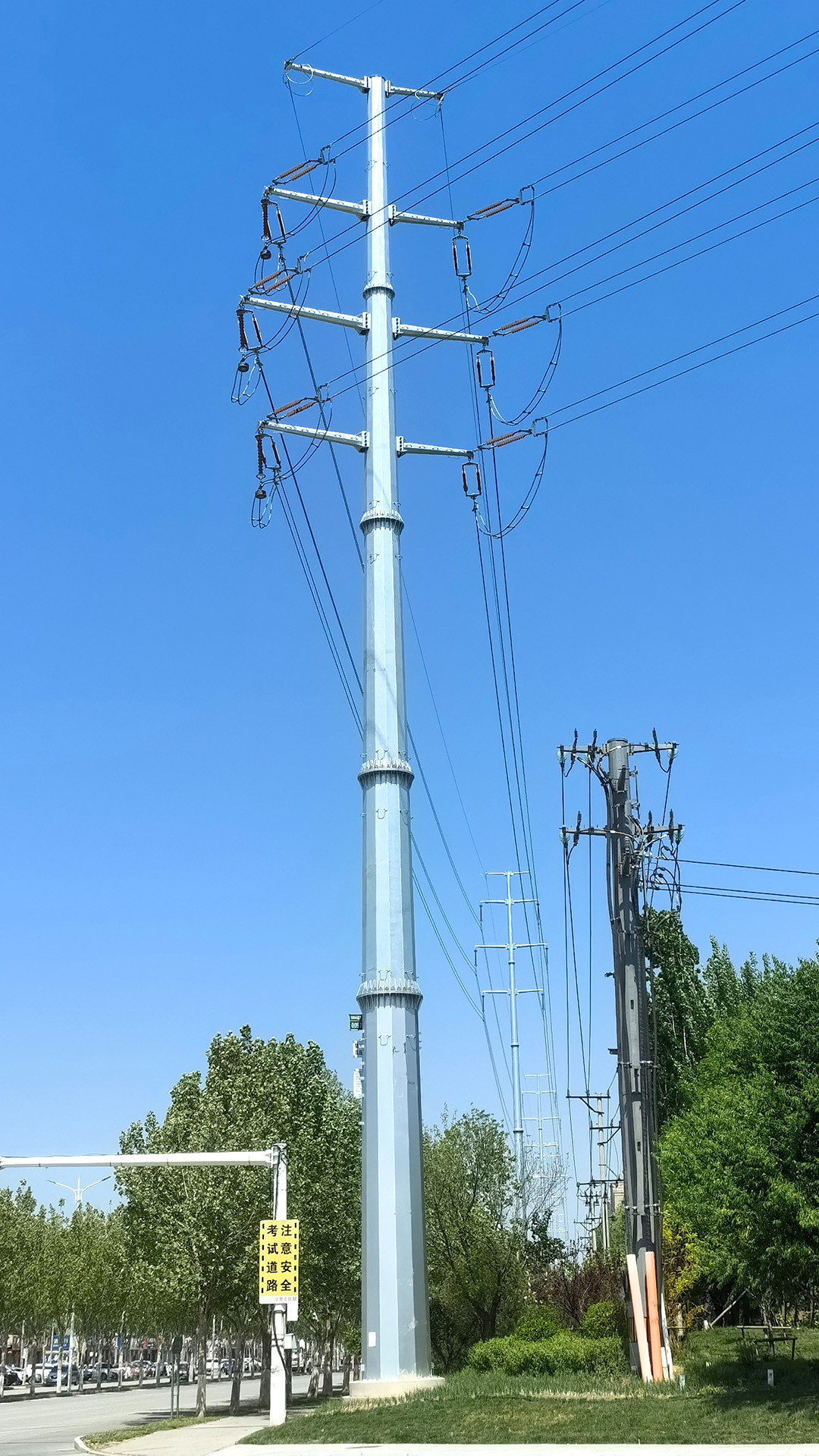
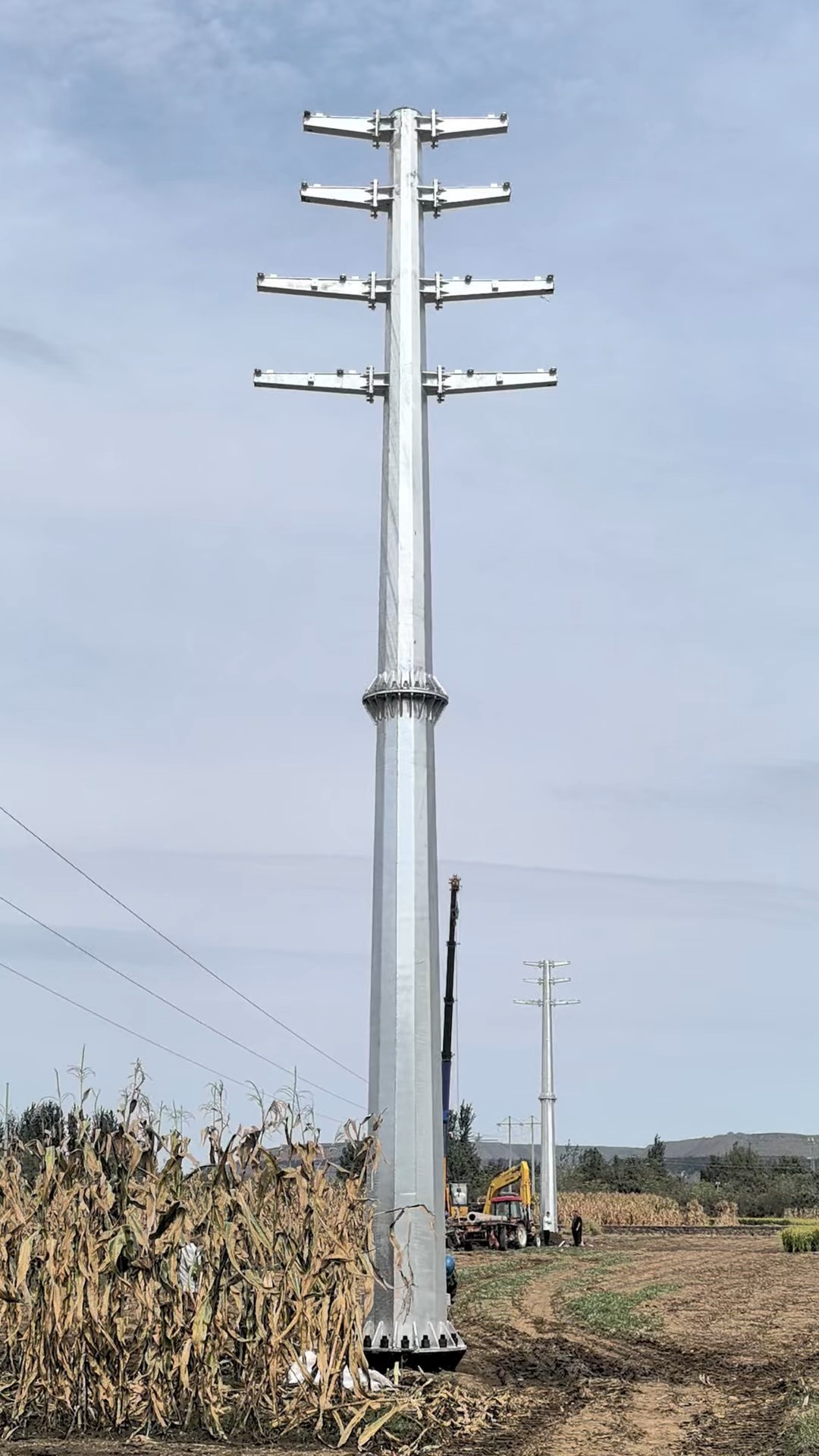
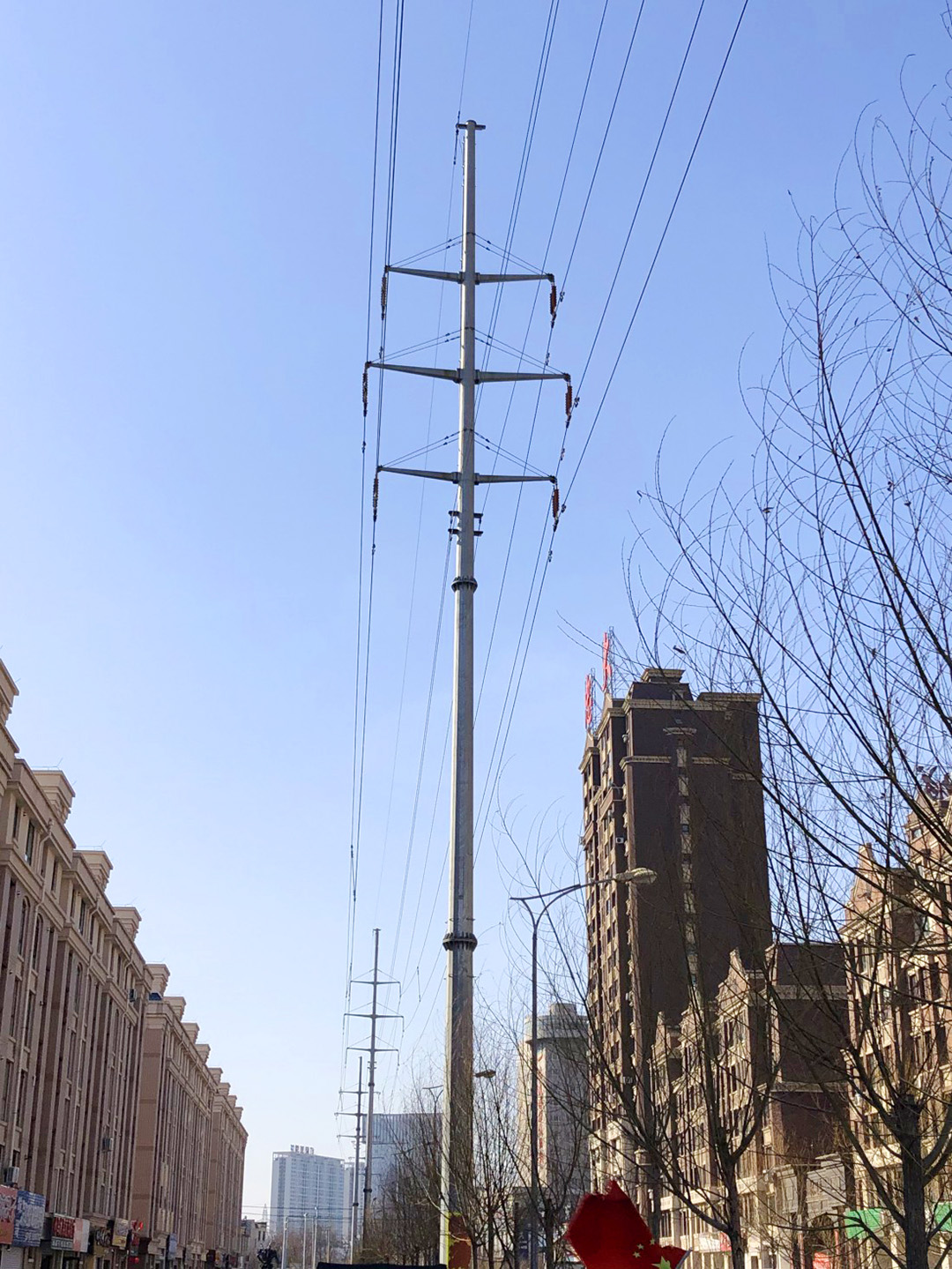




The Role of Tubular Steel Poles in Electrical Power Transmission
Introduction
Electrical power transmission is a cornerstone of modern civilization, enabling the efficient delivery of electricity from generation sites to consumers. As the demand for reliable and resilient electrical infrastructure grows, so does the need for robust and efficient support structures. Tubular steel poles have emerged as an essential component in this domain, offering numerous advantages over traditional materials like wood and concrete. This comprehensive article explores the intricacies of tubular steel poles in electrical power transmission, covering their design, materials, manufacturing processes, applications, benefits, challenges, and future trends.
.
Historical Background
Early Power Transmission Structures
In the early days of electrical power transmission, wooden poles were predominantly used due to their availability and ease of handling. However, wood’s susceptibility to decay, insects, and weathering necessitated frequent replacements and maintenance, leading to increased operational costs and reliability concerns.
Transition to Steel
By the mid-20th century, steel began to replace wood in power transmission structures. Steel’s superior strength, durability, and resistance to environmental factors made it an attractive alternative. Initially, lattice towers were the primary choice for high-voltage transmission lines, but their complex assembly and bulky nature spurred the development of tubular steel poles, which offered a more streamlined and efficient solution.
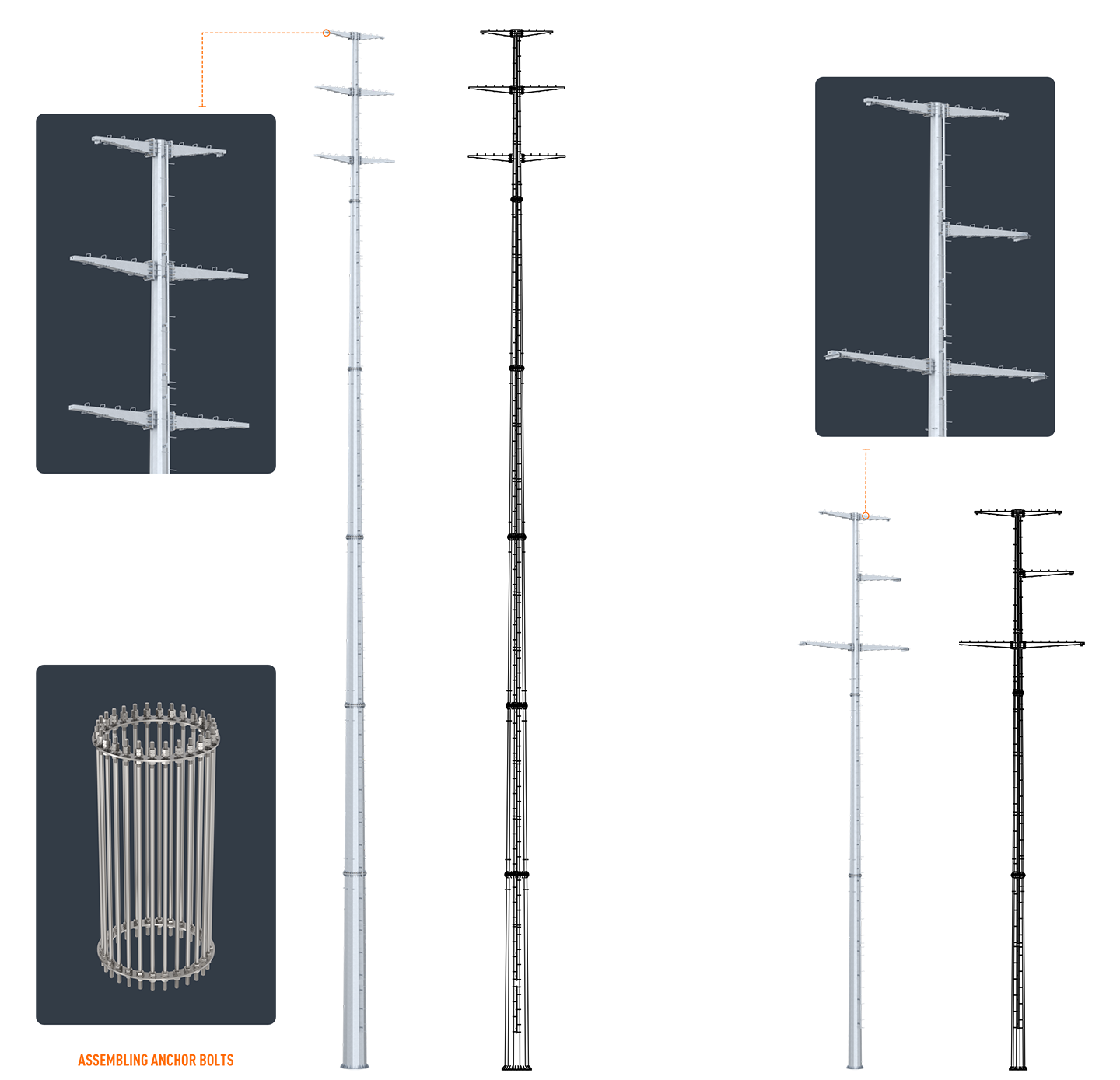
Design and Specifications
Hot Dip Galvanized Steel Tubular Pole
1. Steel materials conform to ASTM A36 with Q345 (S355JR), Q460,etc
2. Welding: Welding complies with CSA and AWS, AWS D1.1 standard. The welders have got corresponding certificate after testing and inspection.
3. Finish: Hot-dip galvanized in accordance with ASTM A123.
4. Pole Height: >16M
5. Pole shape: Conical / Round
6. Type: Straight Pole ,Tensile Pole ,Turn Pole (Double-loop corner pole, Single or double loops/circuit pole, single or double tensile/terminal/straight pole, etc)
7. Resistant: Against earthquake of 8.8 grade. Wind speed as design.
8. Quality Standard: ISO9001:2008, AAA credit rating, etc
9. Easy install and maintenance
10. Voltage:10-550KV
On OD : – ±1% On Specified OD.
Thickness : ±10% of the specified thickness
Overall Length = ± 25 mm
Sectional Length = ± 40 mm
Straightness : 1/600 of length
Weight tolerance: (-10 %)
This series of products can be customized by customers,
The specific price is subject to the reply to the inquiry.
Structural Configurations
Tubular steel poles come in various structural configurations, each tailored to specific needs:
Single-Pole Structures: Typically used for medium-voltage lines and distribution networks, offering a balance between simplicity and strength.
H-Frame Structures: Employed for higher voltage transmission lines, providing enhanced stability and load distribution.
Monopoles: These are single, tall poles designed for high-voltage transmission lines, minimizing land use and visual impact.
Material Selection
The choice of material is critical in ensuring the performance and longevity of tubular steel poles. Commonly used steel grades include:
Q345B/A572 Grade 50: Known for its high strength and resilience.
Q235B/A36: A more economical option for less demanding applications.
High-Performance Alloys: Such as Q460, ASTM A573 Grade 65, and others, used for specialized requirements.
Mechanical Properties
Key mechanical properties of tubular steel poles include:
Yield Strength: Often exceeding 345 MPa, ensuring the poles can withstand substantial loads.
Tensile Strength: Typically ranging from 490 MPa to 620 MPa, crucial for resisting breakage.
Safety Factors: Generally, a safety factor of 2.5 to 3 is applied to account for unexpected loads and environmental conditions.
Surface Treatments
To enhance durability and resistance to corrosion, tubular steel poles undergo various surface treatments:
Hot-Dip Galvanization: Provides a protective zinc coating, following standards such as ASTM A123.
Polyester Powder Coating: Offers additional protection and aesthetic customization.
Specialized Coatings: Developed for extreme environments, including marine and industrial areas.
Manufacturing Process
Material Preparation
The manufacturing process begins with the selection of high-quality steel coils, which are inspected for compliance with stringent specifications. These coils are then cut into sheets of the required dimensions.
Forming and Welding
The steel sheets are formed into cylindrical or polygonal shapes using advanced machinery. Longitudinal welding is performed to join the edges, followed by flange welding and the addition of necessary accessories such as brackets and climbing steps.
Quality Control
Each pole undergoes rigorous quality control checks, including dimensional verification, mechanical testing, and non-destructive testing (NDT) methods like ultrasonic testing (UT) and magnetic particle testing (MPT) to detect any flaws.
Surface Treatment
After quality control, the poles are subjected to surface treatments such as galvanization or powder coating to enhance their durability and resistance to environmental factors.
Final Assembly and Packaging
The final assembly includes the addition of any custom features and thorough inspection before packaging. Poles are then prepared for transportation using protective materials to ensure they arrive at the installation site in optimal condition.
Applications in Electrical Power Transmission
High-Voltage Transmission Lines
Tubular steel poles are extensively used in high-voltage transmission lines, typically ranging from 69 kV to 765 kV. Their high strength-to-weight ratio allows them to support long spans between poles, reducing the number of structures needed and minimizing land use.
Medium-Voltage Distribution Networks
For medium-voltage distribution networks, tubular steel poles provide a reliable and cost-effective solution. They are commonly used in urban and suburban areas, where their aesthetic appeal and compact footprint are advantageous.
Substation Structures
In substations, tubular steel poles support various components such as busbars, transformers, and switching equipment. Their robustness ensures the stability and safety of the substation infrastructure.
Renewable Energy Integration
As renewable energy sources like wind and solar power become more prevalent, tubular steel poles are used to integrate these sources into the grid. They support the transmission lines
that connect renewable energy plants to the main power grid, ensuring a stable and efficient flow of electricity.
Benefits of Tubular Steel Poles in Electrical Power Transmission
Strength and Durability
One of the primary benefits of tubular steel poles is their exceptional strength and durability. Steel’s high tensile strength allows these poles to support heavy loads without bending or breaking. Additionally, the use of high-quality materials and advanced manufacturing processes ensures that these poles can withstand harsh environmental conditions, including high winds, earthquakes, and extreme temperatures.
Longevity
Tubular steel poles have a significantly longer lifespan compared to traditional wooden poles. Properly treated and maintained steel poles can last several decades, reducing the need for frequent replacements and lowering long-term maintenance costs.
Reduced Maintenance
The durability and corrosion resistance of tubular steel poles mean that they require less maintenance over their lifetime. This not only reduces operational costs but also minimizes the environmental impact associated with maintenance activities.
Aesthetic Appeal
In urban and suburban settings, the sleek design of tubular steel poles is often preferred for its aesthetic appeal. These poles can be powder-coated in various colors to blend with the surrounding environment, enhancing the visual harmony of the area.
Cost-Effectiveness
Despite the higher initial cost compared to wooden poles, tubular steel poles are cost-effective in the long run due to their durability, reduced maintenance needs, and extended lifespan. The overall lifecycle cost of using steel poles is often lower, making them a financially sound investment for utilities.
Environmental Benefits
Steel is a highly recyclable material, and the use of tubular steel poles contributes to sustainable practices in construction and infrastructure development. At the end of their lifecycle, steel poles can be recycled and repurposed, reducing the environmental impact of their production and disposal. Furthermore, the longevity and low maintenance requirements of steel poles minimize resource consumption and waste.
Safety and Reliability
The inherent strength and stability of steel make tubular steel poles a safe and reliable choice for supporting critical infrastructure. They are designed to meet stringent safety standards and can withstand a variety of stresses without compromising their structural integrity. This reliability is particularly important in applications such as electrical transmission, where failure can have significant consequences.
Challenges and Considerations
Corrosion and Environmental Exposure
One of the main challenges associated with tubular steel poles is their susceptibility to corrosion, especially in coastal or industrial environments where exposure to salt and pollutants is high. To mitigate this, poles are often treated with protective coatings such as hot-dip galvanization or powder coatings. Regular maintenance and inspections are also necessary to ensure longevity and performance.
Installation and Transportation
The installation and transportation of tubular steel poles can be challenging due to their size and weight. Specialized equipment and skilled labor are required to handle and erect these poles, which can increase project costs. Additionally, logistical considerations such as transportation routes and site access must be carefully planned to avoid delays and complications.
Cost
While tubular steel poles are cost-effective over their lifespan, the initial investment can be significant. This upfront cost can be a barrier for some projects, particularly those with limited budgets. However, the long-term benefits of reduced maintenance and extended service life often justify the initial expense.
Design and Engineering
Designing tubular steel poles requires careful consideration of various factors, including load-bearing capacity, environmental conditions, and safety standards. Engineers must use advanced modeling and simulation tools to ensure that the poles meet all requirements and perform as expected. This process can be complex and time-consuming, but it is essential for ensuring the safety and reliability of the final product.
Case Studies and Examples
Urban Power Distribution in New York City
In New York City, tubular steel poles are extensively used for power distribution. The city’s dense urban environment necessitates infrastructure that is not only robust and reliable but also aesthetically pleasing. Tubular steel poles meet these requirements, providing stable support for power lines while blending seamlessly with the city’s architecture.
High-Voltage Transmission Lines in the Midwest
In the Midwest United States, where high winds and severe weather conditions are common, tubular steel poles are used to support high-voltage transmission lines. These poles provide the necessary strength and durability to ensure reliable power transmission across long distances, minimizing the risk of outages.
Renewable Energy Integration in California
California’s aggressive renewable energy goals have led to the widespread use of tubular steel poles in integrating solar and wind power into the grid. For example, a large solar farm in the Mojave Desert utilizes tubular steel poles to support transmission lines that carry electricity from the solar panels to the main grid. These poles are designed to withstand the harsh desert environment, ensuring the continuous flow of renewable energy.
Future Trends and Innovations
Advanced Materials and Coatings
Ongoing research and development in materials science are leading to the creation of advanced steel alloys and coatings that offer enhanced performance characteristics. These innovations aim to improve the corrosion resistance, strength, and longevity of tubular steel poles. For example, the development of nanostructured coatings could provide superior protection against environmental degradation, extending the lifespan of poles in harsh conditions.
Smart Poles and IoT Integration
The integration of smart technology and Internet of Things (IoT) into tubular steel poles is an emerging trend that promises to revolutionize power transmission infrastructure. Smart poles equipped with sensors can monitor various parameters such as structural health, environmental conditions, and load stresses in real-time. This data can be transmitted to a central system for analysis, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing the likelihood of unexpected failures.
Modular and Prefabricated Designs
Modular and prefabricated designs are gaining popularity due to their ease of transportation and installation. These designs allow for quicker assembly on-site, reducing labor costs and project timelines. Prefabricated sections can be manufactured under controlled conditions, ensuring high quality and consistency. Once on-site, these sections can be quickly assembled, minimizing disruption and speeding up the deployment of power transmission infrastructure.
Sustainable Manufacturing Practices
As sustainability becomes increasingly important, manufacturers are adopting greener production methods for tubular steel poles. This includes using recycled steel, reducing energy consumption during manufacturing, and implementing waste minimization strategies. These practices not only reduce the environmental impact but also align with global efforts to promote sustainable development.
Enhanced Structural Designs
Advancements in computational modeling and simulation are enabling engineers to design tubular steel poles with enhanced structural performance. These designs consider various factors, including wind loads, seismic activity, and load distribution, to optimize the poles’ strength and stability. For instance, new design algorithms can simulate the impact of extreme weather events, ensuring that the poles remain resilient under adverse conditions.
Integration with Renewable Energy
As the push for renewable energy continues, the role of tubular steel poles in supporting renewable energy infrastructure is expected to grow. This includes not only supporting transmission lines but also integrating with renewable energy technologies such as wind turbines and solar arrays. Innovations in design and materials will ensure that these poles can meet the unique challenges posed by renewable energy projects.
Conclusion
Tubular steel poles are indispensable components of modern electrical power transmission infrastructure. Their combination of strength, durability, cost-effectiveness, and aesthetic appeal makes them an ideal choice for a wide range of applications, from high-voltage transmission lines to urban power distribution and renewable energy integration. Despite challenges such as corrosion and initial costs, ongoing innovations in materials science, smart technology, and sustainable manufacturing practices are poised to address these issues, ensuring that tubular steel poles remain a cornerstone of resilient and efficient power transmission systems.
As the demand for reliable and sustainable electrical infrastructure continues to grow, the role of tubular steel poles will become even more critical. Their ability to be customized for specific needs, coupled with their long lifespan and low maintenance requirements, makes them a cost-effective and sustainable choice for engineers and planners. In summary, tubular steel poles are not just structural elements but vital enablers of modern life, supporting the critical functions that keep our cities, industries, and communities running smoothly. With continued investment in research and development, these poles will undoubtedly play an even more significant role in shaping the future of global infrastructure.
References
IEEE Power & Energy Society. (2020). Standards for Electrical Transmission Structures.
American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE). (2018). Manuals of Practice: Steel Transmission Pole Structures.
National Association of Corrosion Engineers (NACE). (2019). Corrosion Protection Guidelines for Steel Structures.
U.S. Department of Energy. (2022). State of the Grid: Reliability and Resilience.
International Journal of Steel Structures. (2021). Advances in Tubular Steel Pole Design and Materials.
By understanding and leveraging the strengths of tubular steel poles, the power transmission industry can continue to build resilient, efficient, and sustainable infrastructure that meets the needs of the modern world.
Tags: Quality Galvanized Pole
 English
English


